pitifulVM 源码分析
pitifulVM 正如名字所说,是一个用C语言实现的简单的java虚拟机。 源代码在jserv/pitifulvm
运行流程
我们第一步先来看该虚拟机的运行流程。
- 首先按照输入的参数打开java的
.class字节码文件流。
FILE *class_file = fopen(argv[1], "r");
assert(class_file && "Failed to open file");这里用到了一个函数assert,该函数被定义在头文件assert.h中。其主要作用类似于if,当该函数的参数为true时,该函数不起作用。当该函数的参数为false时,则该函数终止程序运行并输出错误信息。类似于:
if(假设不成立)
{
报错&&终止程序!(避免由程序运行引起更大的错误)
}- 将class字节码文件载入内存
class_file_t clazz = get_class(class_file);
int error = fclose(class_file);
assert(!error && "Failed to close file");- 从字节码文件中寻找main方法入口代码
method_t *main_method =
find_method("main", "([Ljava/lang/String;)V", &clazz); // 从字节码中获取入口方法的指针
assert(main_method && "Missing main() method");- 执行代码,但是此处有一个问题,如注释所说目前该vjm缺少lang包
/* FIXME: locals[0] contains a reference to String[] args, but right now
* we lack of the support for java.lang.Object. Leave it uninitialized.
*/
int32_t locals[main_method->code.max_locals];
int32_t *result = execute(main_method, locals, &clazz);
assert(!result && "main() should return void");以上就是pitifulVM的主要运行流程。下面开始按步骤分析。
字节码载入内存
数据类型 class_file_t
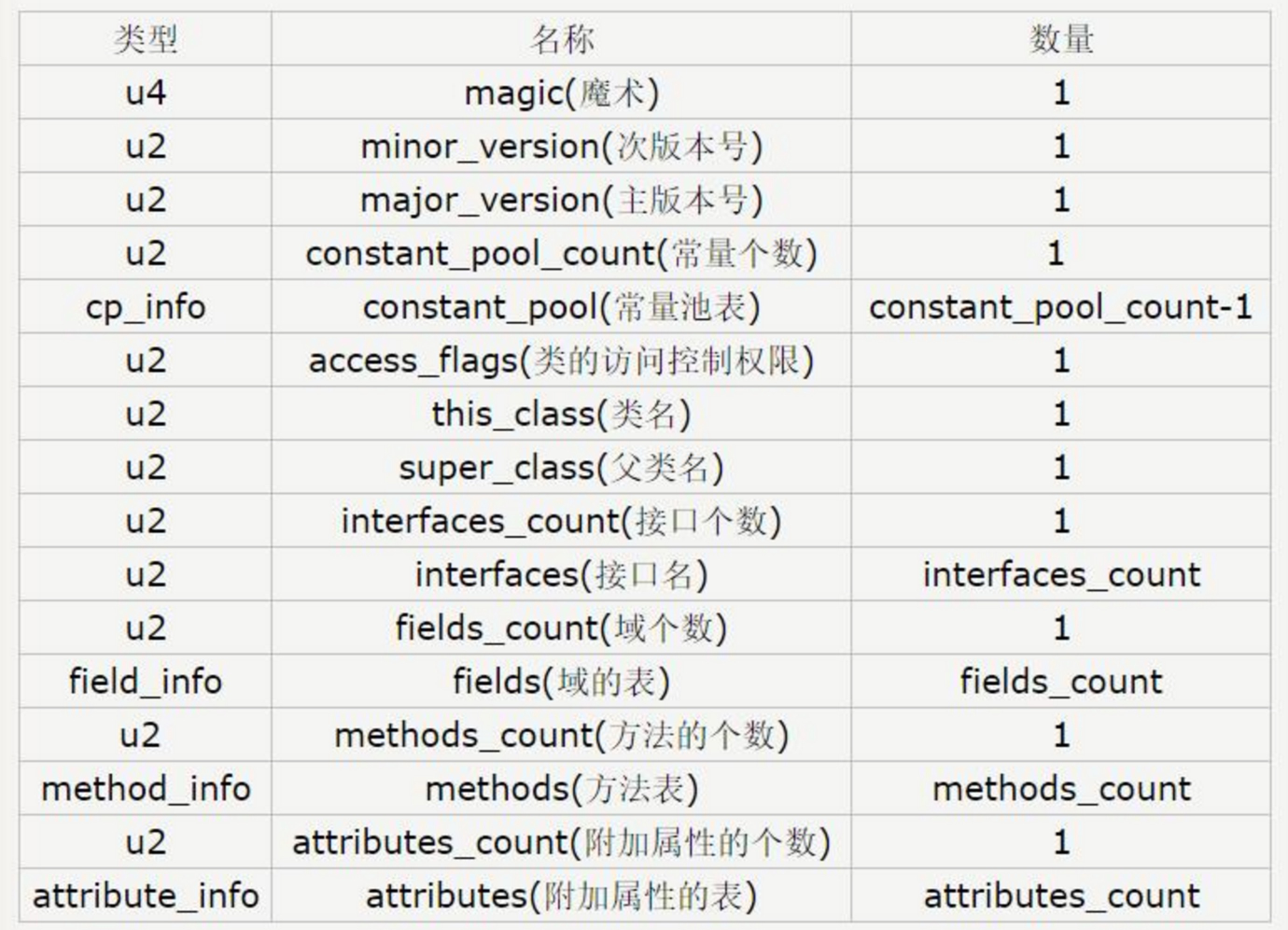
从第三步来看class_file_t clazz = get_class(class_file);,pitifulVM定义了一个数据类型 ’字节码文件’。我们来具体看这个数据类型。我们将之和正常的class字节码文件结构相比较。
typedef struct {
constant_pool_t constant_pool;
method_t *methods; // 方法表
} class_file_t;尤其定义可知,pitifulVM主要分为两部分,常量池部分与方法部分,这是java程序运行所用到的两个主要文件。
这是字节码文件所含的全部信息。对比两个结构,猜测pitifulVM可能会缺失访问权限控制部分的功能。
继续分析constant_pool_t 和method_t的结构;
constant_pool_t 常量池
该数据类型中包含常量池个数和常量池表,u2所对应的数据类型是uint16_t无符号16位整型。
typedef struct {
u2 constant_pool_count; //uint16_t 常量池计数器
const_pool_info *constant_pool; //常量池表
} constant_pool_t;const_pool_info
常量池表中每一项的数据类型如下:
typedef struct {
const_pool_tag_t tag; // java中数据类型的数值表示,具体如下图
u1 *info; // uint8_t 常量的详细信息,如字节程度,索引,所在class,具体内容等
} const_pool_info;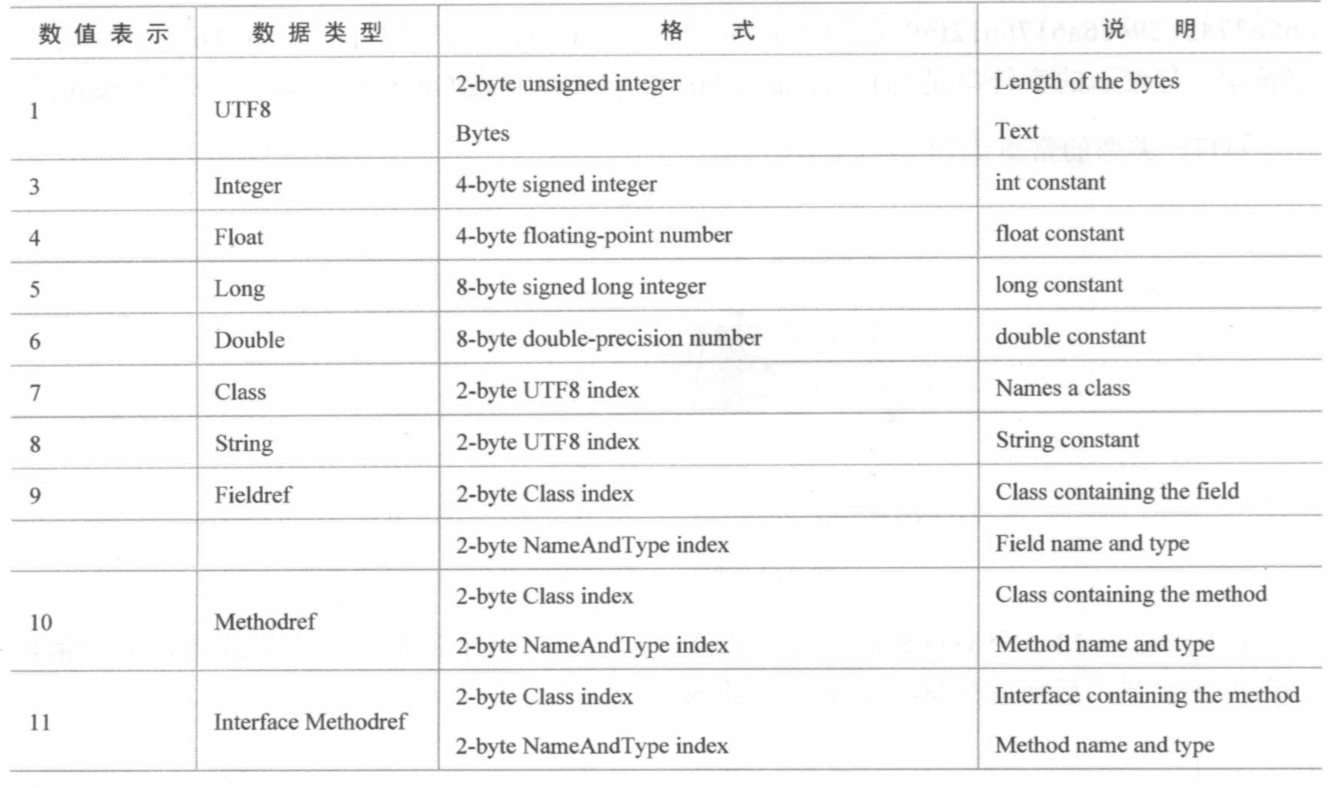

method_t 方法
在这里看到,“方法” 数据结构,所以在pitifulVM中没有实现方法计数器,可能会用sizeof()等方法代替。
typedef struct {
char *name;
char *descriptor;
code_t code; // 方法里的java代码,可能没有属性表attributes
} method_t;code_t
typedef struct {
u2 max_stack;
u2 max_locals;
u4 code_length;
u1 *code;
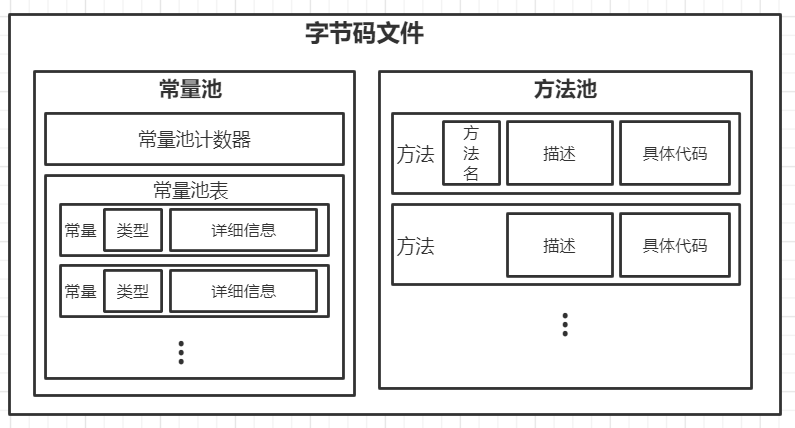
} code_t;至此,数据类型 class_file_t 分析结束,关系图如下:
方法 get_class()
代码如下:
class_file_t get_class(FILE *class_file)
{
/* Read the leading header of the class file */
get_class_header(class_file);
/* Read the constant pool */
class_file_t clazz = {.constant_pool = get_constant_pool(class_file)};
/* Read information about the class that was compiled. */
get_class_info(class_file);
/* Read the list of static methods */
clazz.methods = get_methods(class_file, &clazz.constant_pool);
return clazz;
}方法 get_class_header()
java字节码文件结构如图所示:
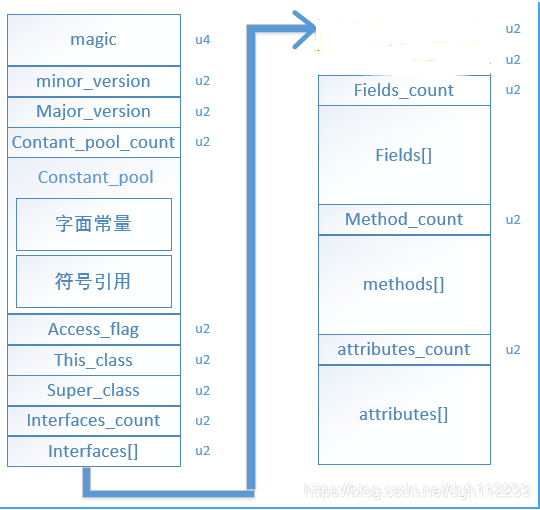
猜测该函数功能就仅仅是转移文件头指针到 class_file_t的第一个结构常量池部分,大概就是一次偏移u4(魔术)+u2(次版本号),u2(主版本号)
代码如下:
class_header_t get_class_header(FILE *class_file)
{
return (class_header_t){
.magic = read_u4(class_file),
.major_version = read_u2(class_file),
.minor_version = read_u2(class_file),
};
}该函数的返回值为一个新的数据类型:class_header_t,定义如下:
class_header_t
typedef struct {
u4 magic;
u2 minor_version;
u2 major_version;
} class_header_t;由于pitifulVM中的字节码数据类型不包含文件头的校验,所以这一部分的返回值没有被储存,只起到转移头指针的作用。(没有安全校验,可能会有风险)
方法 get_constant_pool()
这里是整个get_class()方法的重头戏,代码太多,分结构放上来。
- 读取常量池计数器,为常量池动态分配内存。
constant_pool_t cp = {
/* Constant pool count includes unused constant at index 0 */
.constant_pool_count = read_u2(class_file) - 1,
.constant_pool =
malloc(sizeof(const_pool_info) * cp.constant_pool_count),
};
assert(cp.constant_pool && "Failed to allocate constant pool");- 接下来就是处理字节码文件常量池中的数据了,冗长的代码,但思路很简单。
const_pool_info *constant = cp.constant_pool; // 获取结构体常量池指针,这里没有实际的作用,作用大概就是简化代码吧
for (u2 i = 0; i < cp.constant_pool_count; i++, constant++) {
constant->tag = read_u1(class_file);
switch (constant->tag) { // 通过const_pool_tag_t中的数值判断java常量的数据类型
case CONSTANT_Utf8: { // utf-8 字符串
u2 length = read_u2(class_file);
char *value = malloc(length + 1);
assert(value && "Failed to allocate UTF8 constant");
size_t bytes_read = fread(value, 1, length, class_file);
assert(bytes_read == length && "Failed to read UTF8 constant");
value[length] = '\0';
constant->info = (u1 *) value;
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Integer: { // 整形字面量
CONSTANT_Integer_info *value = malloc(sizeof(*value));
assert(value && "Failed to allocate integer constant");
value->bytes = read_u4(class_file);
constant->info = (u1 *) value;
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Class: { // 类引用
CONSTANT_Class_info *value = malloc(sizeof(*value));
assert(value && "Failed to allocate class constant");
value->string_index = read_u2(class_file);
constant->info = (u1 *) value;
break;
}
case CONSTANT_MethodRef: // 类方法的符号的引用
case CONSTANT_FieldRef: { // 字段的符号的引用 数据结构一样,所以合并
CONSTANT_FieldOrMethodRef_info *value = malloc(sizeof(*value));
assert(value && "Failed to allocate FieldRef or MethodRef constant");
value->class_index = read_u2(class_file);
value->name_and_type_index = read_u2(class_file);
constant->info = (u1 *) value;
break;
}
case CONSTANT_NameAndType: { // 字段方法的名称及类型
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info *value = malloc(sizeof(*value));
assert(value && "Failed to allocate NameAndType constant");
value->name_index = read_u2(class_file);
value->descriptor_index = read_u2(class_file);
constant->info = (u1 *) value;
break;
}
default:
fprintf(stderr, "Unknown constant type %d\n", constant->tag);
exit(1);
}
}对比一下看缺少什么类型。


目前没有实现的类型:浮点型,双精度浮点型,长整型,字符串。
方法 get_class_info()
代码如下:同样是由于目前的字节码数据结构不包含以下字段,所以仅仅起到移动文件头指针的作用。并且可以看出,目前pitifulVM 不支持接口与继承
class_info_t get_class_info(FILE *class_file)
{
class_info_t info = {
.access_flags = read_u2(class_file),
.this_class = read_u2(class_file),
.super_class = read_u2(class_file),
};
u2 interfaces_count = read_u2(class_file);
assert(!interfaces_count && "This VM does not support interfaces.");
u2 fields_count = read_u2(class_file);
assert(!fields_count && "This VM does not support fields.");
return info;
}方法 get_methods()
代码如下:
method_t *get_methods(FILE *class_file, constant_pool_t *cp)
{
u2 method_count = read_u2(class_file); // 读取方法表计数器
method_t *methods = malloc(sizeof(*methods) * (method_count + 1)); // 动态分配方法表大小
assert(methods && "Failed to allocate methods");
method_t *method = methods;
for (u2 i = 0; i < method_count; i++, method++) {
method_info info = {
.access_flags = read_u2(class_file),
.name_index = read_u2(class_file),
.descriptor_index = read_u2(class_file),
.attributes_count = read_u2(class_file),
};
const_pool_info *name = get_constant(cp, info.name_index); // 从常量池中取出方法名常量
assert(name->tag == CONSTANT_Utf8 && "Expected a UTF8");
method->name = (char *) name->info;
const_pool_info *descriptor = get_constant(cp, info.descriptor_index);// 从常量池中取出方法描述常量
assert(descriptor->tag == CONSTANT_Utf8 && "Expected a UTF8");
method->descriptor = (char *) descriptor->info;
/* FIXME: this VM can only execute static methods, while every class
* has a constructor method <init>
*/
if (strcmp(method->name, "<init>")) // 判断是否有非静态成员变量和非静态方法
assert((info.access_flags & IS_STATIC) &&
"Only static methods are supported by this VM.");
read_method_attributes(class_file, &info, &method->code, cp);
}
/* Mark end of array with NULL name */
method->name = NULL;
return methods;
}<init>是实例构造器,用来对非静态变量解析初始化,由于vm不支持<init>方法,因此说明该vm执行的java文件不能含有非静态成员变量和方法。<cinit>负责class类构造器对静态变量,静态代码块进行初始化。
获取入口方法指针
方法 find_method()
method_t *find_method(const char *name, const char *desc, class_file_t *clazz)
{
for (method_t *method = clazz->methods; method->name; method++) {
if (!(strcmp(name, method->name) || strcmp(desc, method->descriptor)))
return method;
}
return NULL;
}执行代码
方法 execute()
int32_t *execute(method_t *method, int32_t *locals, class_file_t *clazz)
{
code_t code = method->code; // 获取方法
int32_t op_stack[code.max_stack]; // 创建操作数栈
uint32_t op_count = 0; // 操作数栈的深度计数器,也就是栈顶指针
/* position at the program to be run */
uint32_t pc = 0; // pc计数器
uint8_t *code_buf = code.code; // 方法的jvm代码
int loop_count = 0;
while (pc < code.code_length) { // 执行代码
loop_count += 1;
uint8_t current = code_buf[pc]; // 通过pc计数器读取当前代码
/* Reference:
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_bytecode_instruction_listings
*/
switch (current) { // 处理当前代码
/* Return int from method */
case i_ireturn: { // 从方法中返回int类型的数据
...
} break;
/* Return void from method */
case i_return: // 从方法中返回,返回值为void
return NULL;
/* Invoke a class (static) method */
case i_invokestatic: { // 调用静态方法
uint8_t param1 = code_buf[pc + 1], param2 = code_buf[pc + 2]; // 读取源操作数和目标操作数
uint16_t index = ((param1 << 8) | param2); // 计算调用的方法的地址
/* the method to be called */
method_t *own_method = find_method_from_index(index, clazz); // 获取到要调用的方法
uint16_t num_params = get_number_of_parameters(own_method); // 获取参数个数
int32_t own_locals[own_method->code.max_locals];
for (int i = num_params - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 取参数
own_locals[i] = op_stack[op_count - 1];
op_count -= 1;
}
int32_t *exec_res = execute(own_method, own_locals, clazz); // 调用方法
if (exec_res) {
op_stack[op_count] = *exec_res;
op_count += 1;
}
free(exec_res); // 释放对象
pc += 3; // pc 寄存器自增
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison with zero succeeds: if equals */
case i_ifeq: { // 如果等于0,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison with zero succeeds: if not equals */
case i_ifne: { // 如果不等于0,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison with zero succeeds: if less than 0 */
case i_iflt: { // 如果小于0,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison with zero succeeds: if >= 0 */
case i_ifge: { // 如果大于等于0,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison with zero succeeds: if greater than 0 */
case i_ifgt: { // 如果大于0,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison with zero succeeds: if <= 0 */
case i_ifle: { // 如果小于等于0,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison succeeds: if equals */
case i_if_icmpeq: { // 如果两个int值相等,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison succeeds: if not equals */
case i_if_icmpne: { // 如果两个int类型值不相等,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison succeeds: if less than */
case i_if_icmplt: { //如果一个int类型值小于另外一个int类型值,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison succeeds: if greater than or equal to */
case i_if_icmpge: { // 如果一个int类型值大于或者等于另外一个int类型值,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison succeeds: if greater than */
case i_if_icmpgt: { // 如果一个int类型值大于另外一个int类型值,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch if int comparison succeeds: if less than or equal to */
case i_if_icmple: { //如果一个int类型值小于或者等于另外一个int类型值,则跳转
...
} break;
/* Branch always */
case i_goto: { //无条件跳转
...
} break;
/* Push item from run-time constant pool */
case i_ldc: { //常数到操作数栈
...
} break;
/* Load int from local variable */
case i_iload_0: // 变量到操作数栈
case i_iload_1:
case i_iload_2:
case i_iload_3: {
...
} break;
/* Load int from local variable */
case i_iload: { //变量到操作数栈
...
} break;
/* Store int into local variable */
case i_istore: { // 操作数栈到变量
...
} break;
/* Store int into local variable */
case i_istore_0:
case i_istore_1:
case i_istore_2:
case i_istore_3: { //操作数栈到变量
...
} break;
/* Increment local variable by constant */
case i_iinc: { // 把一个常量值加到一个int类型的局部变量上
...
} break;
/* Push byte */
case i_bipush: { // 常数到操作数栈
...
} break;
/* Add int */
case i_iadd: { // 加
...
} break;
/* Subtract int */
case i_isub: { // 减
...
} break;
/* Multiply int */
case i_imul: { //乘
...
} break;
/* Divide int */
case i_idiv: { // 除
...
} break;
/* Remainder int */
case i_irem: { //余数
...
} break;
/* Negate int */
case i_ineg: { //负数
...
} break;
/* Get static field from class */
case i_getstatic: { // 访问类的域和类实例域 未实现
/* FIXME: unimplemented */
pc += 3;
} break;
/* Invoke instance method; dispatch based on class */
case i_invokevirtual: { //调度对象的实便方法
...
} break;
/* Push int constant */
case i_iconst_m1: // 将int类型常量n压入栈
case i_iconst_0:
case i_iconst_1:
case i_iconst_2:
case i_iconst_3:
case i_iconst_4:
case i_iconst_5: {
...
} break;
/* Push short */
case i_sipush: { // 常数到操作数栈
...
} break;
}
}
return NULL;
}正常jvm结构

与pitifulVM 相比,类加载子系统是 get_class方法,执行引擎是execute方法,没有堆。实现了方法区,栈,PC,没有GC。